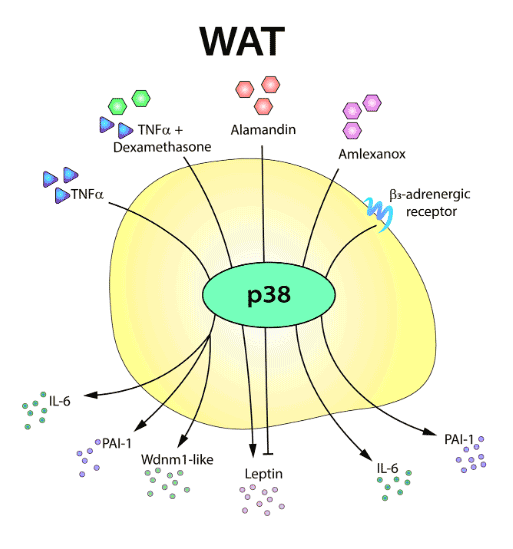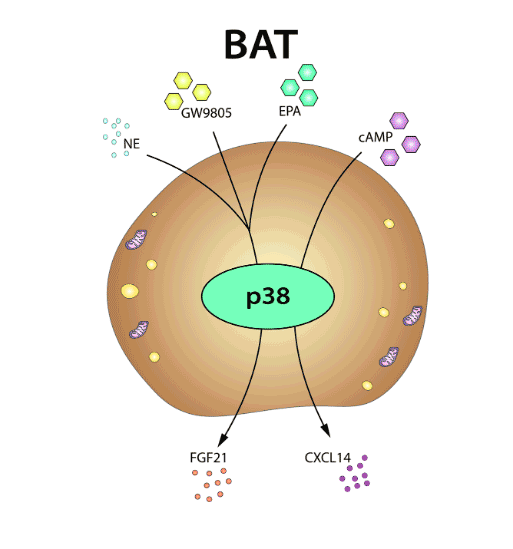
We are seeking a highly motivated candidate, who would like to start a scientific career doing their doctoral thesis working in understanding p38 kinases role in how the communiation between organs affect the metabolic. This work will be supervised by Dr. Guadalupe Sabio.
We offer incorporation to CNIC via an FPU predoctoral contract. Interested candidates will need to apply before 19 September 2023 in the following CNIC website:
METABOkines: Comunicación celular en el metabolismo: Implicación de la vía de las p38s.
PID2022-138525OB-I00
ELEGIBILITY CRITERIA
- This call is open to applicants from all nationalities holding a Master’s degree in Biomedical Sciences.
- An excellent academic record and previous research experience during their undergraduate period will be valued very positively.
- Authorship of publicacions in indexed journal will be valued very positively.
- Candidates must have a solid working knowledge of English.